Domain addresses on the dark web typically use non-standard top-level domains like “.onion” instead of common extensions like “.com” or “.org,” making them inaccessible through conventional browsers. These hidden networks intentionally conceal IP addresses and encrypt communications through multiple layers of routing. Understanding the relationship between Tor and the dark web is essential—Tor (The Onion Router) is the primary software used to access these hidden sites. Discover the key differences between the Dark Web and Deep Web, their uses and risks to businesses.
What Precautions Should Be Taken When Accessing The Dark Web?
Using Tor to import and export data comes with end-to-end encryption, which makes it impossible to track the user data since it works anonymously. If you decide to venture into the dark depths of the deep web, make sure you’ve bolstered your device’s security with powerful privacy and security tools that can defend against dark web threats. Clarify the difference between dark web and deep web—and safeguard both.
Indicators Of Compromise In Threat Intelligence
The benefit of using Tor to surf the regular internet is that your activities will be private. Thanks to a strong layer of encryption, your ISP cannot know which websites you’re visiting. The dark web is a smaller, intentionally hidden part of the internet that requires special software (like the Tor browser or I2P) to access. It is designed to provide anonymity to both users and site operators. Lastly, the “dark web” is a different category of the Internet and is sometimes confused as part of the deep web.
How CrowdStrike Protects You From Illegal Dark Web Activity

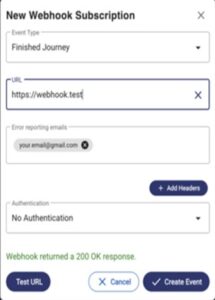
Ideally, you should have a separate anonymous identity for each substantial outing on the dark web. But a single set is generally enough if it’s just about one or a few “informational” visits. A discrete online identity, which has nothing to do with your present one. Separate email, phone number, anonymous payment channel,…..the list can be long based on what you aspire to get involved with on the dark web.
How Does The Deep Web Impact Data Accessibility?
This enables the fetching of responses to queries sent by you and me. Simply put, search engines use software (called crawlers or web spiders) that visit all sites and send them for indexing. If a particular website does not allow the crawlers to send the data for indexing, the site is not indexed and hence, cannot be seen on search engines. Behind the anonymity of the censor-resistant platforms, Dark Web has flourished a thriving trade of all that is illegal and unacceptable in civil society. In their book Cryptopolitik and the Darknet, researchers Daniel Moore and Thomas Rid claimed that around 57% of the Dark Web includes illicit content.
What Is The Primary Difference Between The Deep Web And The Dark Web?
Some well-known underground sources can be easier to find because there are dedicated sites that share links and maintain regular status updates. But in many cases, finding the exact URLs through manual search methods can be next to impossible. The Gray Web, Deep Web, and Dark Web are all valuable sources of threat intelligence, but many organizations limit their information-gathering efforts to the Surface Web. Expanding their reach – through the use of Dark Web monitoring tools – can be invaluable to a corporate cybersecurity and risk management program. It enables people to host websites selling illegally-obtained credit cards and social security numbers, counterfeit money, forged documents, weapons, and drugs and is even used for criminal activities.

Accessing Dark Web Sites

While both the dark and deep web represent parts of the internet that fall outside the scope of traditional search engines, they differ in accessibility, use cases, and the types of threats they expose. Unlike the dark web, you don’t need any special software to access the deep web and can use your usual browser. It may, however, require a username or password for authentication. However, the Dark Web isn’t all bad, and, in fact, the technology that makes it possible, Tor, was originally created by the U.S. government for legitimate purposes.
Security Threats
This leaked data helps hackers and other cybercriminals get the info needed for identity theft, stuffing attacks and nefarious activities of all kinds. For example, journalists who researched the dark web were shocked to find that it already had lots of info on them. The dark web presents various threats, including malicious software and computer viruses, posing risks to users’ systems and data security. Users also face the potential danger of government monitoring and surveillance — or scams and fraud, and other activities that can lead to financial loss and identity theft. On the Deep Web, these risks primarily relate to the fact that you need to authenticate to access a private site and that these sites contain a great deal of sensitive and valuable personal data. If your password or other credentials are the key to unlocking this data, then cybercriminals will attempt to steal these credentials via phishing, social engineering, malware, and other means.
Misconception 2: “All Dark Web Activity Is Illegal”
As mentioned earlier, regular browsers cannot access dark web websites. The dark web uses “The Onion Router” hidden service protocol to function. Tor servers are used for surfing; they are undetectable from search engines and offer users complete anonymity.
- The dark web is a subsegment of the deep web that can only be accessed with special tools, such as the Tor browser.
- It is absolutely critical to know if your information is on the dark web in order to properly protect yourself from threats.
- Unlike the surface web, which is easily accessible and often serves legitimate purposes, the deep web holds valuable information that typically requires specific access credentials or subscriptions.
- The anonymity provided by the dark web does indeed make it ideal for people looking to engage in illicit activity.
But at this point, you have read the article and learned the basics. Perhaps that has awoken you to the need to maintain your privacy and security on all of those webs? If you watched a single procedural TV series recently, they definitely featured at least a single internet-heavy episode.
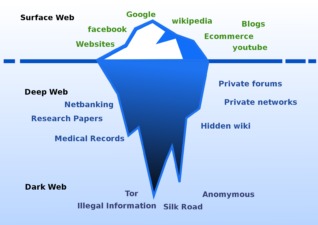
The deep web, also known as the hidden web, is the part of the internet where almost all online activity happens. The deep web consists of sites and databases that are not fully accessible to standard search engines such as Google, Bing and Yahoo. This could be because the pages are not indexed, meaning they can’t be found by searching for them on search engines, they are paywalled websites or private databases. To access deep web content, you’ll need the direct link or sign-in credentials that grant you access to it.
The deep web is a subset of the web containing websites that cannot be located by search engines. Anything that does not show up on Google can be found on the deep web. Search engines crawl the internet through links, visiting one web page, the links on that page and so on, keeping track of all the information. What cannot be accessed by search engines is referred to as part of the deep web. The internet’s deeper layers—namely, the deep web and dark web—represent distinctly different realms of online interaction.