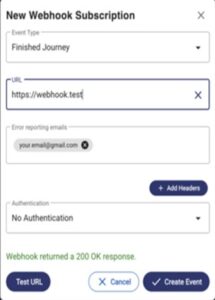
Law enforcement shutdowns are also only one type of disruption that dark web communities face. These included an advanced encryption program known as “Pretty Good Privacy” and a cryptocurrency called Monero. Unlike Bitcoin, which records every payment on a public ledger, Monero conceals all transaction details by default, which makes them nearly impossible to trace. Last week, one of the dark web’s most prominent drug marketplaces—Archetyp—was shut down in an international, multi-agency law enforcement operation following years of investigations.
There are many initiatives and programs aimed at teaching the public about the risks and how to stay safe, such as cybersecurity workshops and online courses designed to educate and inform. These efforts help folks learn how to secure their personal information, recognize suspicious activity, and take preventative measures. The risk of data breaches is higher than ever for businesses, potentially leading to financial loss, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Individuals are also at risk, as their personal information can be exploited for identity theft or sold multiple times over. Dark web markets work in a way that is not like your everyday online shopping.
What Are The Risks Of Using Dark Markets?

Plus, there’s a thorough vetting process for new buyers and sellers to keep the community more secure. In a way, it feels more like a private club than an open market, and that’s exactly how the operators want it. Chainalysis data shows darknet marketplace revenue dropped post-Hydra seizure in 2022 but recovered to $2 billion in Bitcoin inflows during 2024 Darknet market BTC inflow drop and shift to Monero. Abacus alone represented nearly 5 per cent of total DNM revenue, underscoring the ongoing scale of underground commerce. Archetyp’s takedown might make headlines, but it won’t stop the trade of illicit drugs on the dark web. It should force us to think about where harm is really happening online and whether current strategies are looking in the wrong direction.
- These features help establish trust between buyers and sellers, providing users with a sense of security that many other markets lack.
- Dark web websites look pretty much like any other site, but there are important differences.
- Unique threads discussing drainers on dark web forums increased from 55 in 2022 to 129 in 2024, with Telegram channels serving as prominent hubs for these activities.
- Sure, you might come across listings for legit products like handcrafted jewelry or digital art, but those are few and far between.
- Illicit drug sales, for example, are promoted on social media, where platform features such as recommendation systems are affording new means of illicit drug supply.
Typical Use-Cases Of Dark-Web Marketplaces In 2025
Launched in 2023, STYX focuses on financial crime, providing stolen credit card data, hacked bank accounts and access to various cryptocurrency laundering tools. Some are looking for illegal stuff they can’t buy elsewhere, like drugs or counterfeit documents. Despite growing crackdowns from law enforcement agencies, the dark web remains a hotbed of criminal activity, offering everything from drugs to stolen data.
Abacus Upgrades

Operations such as the takedown of the Silk Road and AlphaBay marketplaces demonstrate the global effort required to dismantle these illicit networks. However, combating dark web crime demands cooperation between businesses, governments, and technology providers to address emerging threats and protect the integrity of data. To protect against the threats posed by the dark web, businesses must adopt a proactive and multi-layered cybersecurity strategy.
Safe Dark Web Links To Explore
In 2025, 95% of markets prefer XMR over BTC’s public ledger, with transaction volume up 60% since 2023. ProPublica is an investigative news site owned by an independent nonprofit that exposes abuses of power and corruption. It hosts an onion site so people in countries with restricted press freedom can access its journalism, which covers everything from hacktivism to government repression. Bitcoin’s blockchain is too leaky these days, and markets like Archetyp going Monero-only prove it. Mixers help, sure, but XMR’s built-in privacy is why I’ve switched my stash over.
Leverage Free Cybersecurity Resources
Therefore, you must know how to access dark web marketplaces safely (covered later in this article). ASAP is a tech nerd’s playground—accepting BTC, LTC, ZCash, and Monero, it’s got options for days. Their DeadDrop system’s a standout—vendors stash your goods IRL, no mailing hassles—and wallet-less payments mean no one’s bolting with your cash, a relief after I got burned once by a shady escrow dodge. Listings aren’t public, but it’s steady—think drugs (weed, pills, some synthetics), a few digital extras like cracked accounts.
Top 7 Dark Web Marketplaces
It features over 40,000 listings including narcotics, counterfeit items, hacking tools, and stolen data. The marketplace is well-known for its bug bounty programs and robust security mechanisms, including mandatory 2FA. This can include everything from full names, email logins, and passwords to credit card details, social security numbers, and bank account information.

Hence, it should be the top priority to track these platforms and shut them down as quickly as possible. The buyers, or “consumers,” are cybercriminals who use these tools to launch illegal activities. The victims, who are common users, businesses, and even banks, who end up paying the price. Some vendors offer services to help people “clean” illegally obtained funds using cryptocurrency and fake transactions. They mix and transfer funds through various privacy wallets and escrow services to hide the original source and make the illicit transactions harder to trace.

First, in the USA, it is a federal offense to use the USPS for any of these transactions. If the buyer or seller gets caught, there are significant legal ramifications. Many of these markets operate internationally, and some have certain specialties. The .onion top-level domain (TLD) name is the dark web’s version of “.com” or “.net”. Unlike traditional TLDs, servers using the onion TLD are more difficult to locate. This makes it more difficult for authorities to locate and take down these sites.

It has a search option to let you find local and international products and services on the dark web. A lot of vendors from all over the world are registered here, offering an extensive range of products, including digital services, security tools, and other equipment. For those who are looking for a reliable Alphabay Market alternative, Awazon Market aspires to become the solution. Of course, not all the popular and widely-used dark web sites and things like marketplaces on the dark net are illegal. Some use them due to privacy concerns, such as journalists talking to informants or whistleblowers, while others may simply want to protect their confidential information from observation or tracking. Nevertheless, most people on the internet do not need to communicate or venture into the dark web.
Top 10 Dark Web Markets
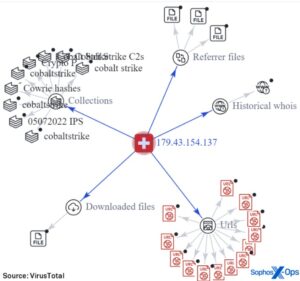
One of the German officers charged with analyzing the contents of the CyberBunker servers told me that the volume of data was unwieldy, but its content fascinating. “I do not recall any case where this huge amount of criminal-infrastructure data was gathered,” he said. In 2025, this trend is expected to continue, pushing cybercriminals to adopt more sophisticated and anonymous operating models, such as closed, invitation-only forums. Cybercriminals are expected to exploit trusted company-contractor relationships, breaching contractor systems to access corporate data. This tactic, seen in 2024 with incidents involving Ticketmaster and IntelBroker, could lead to an overall rise in data breaches. The number of malicious tools, or “drainers,” designed to steal cryptocurrency assets like tokens and NFTs saw a substantial rise.
Following stricter bans on Telegram channels hosting cybercriminals, experts predict a resurgence of activity on dark web forums. Black traffic schemes—malicious landing pages promoted via deceptive ads—remained a constant threat. These schemes leveraged mainstream ad platforms to distribute malware to unsuspecting users.